
© Thomas Kunz 2000
SCE 574
179
Process Model
äProcess model:
states
äRunning
äBlocked
äReady
äScheduler (kernel) is lowest level of the operating system
äHandles all the
interrupts
äDoes context
switching
äHandles interprocess
communication
äRest of OS is on top
of the scheduler (kernel) implemented as
processes
äFor example
äWhen a disk
interrupt occurs
äThe system stops
running the current process
äMakes the disk
process, which was blocked waiting for the
interrupt, ready to run
äRuns another process
(possibly resuming the original process)
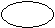
Running

Blocked

Ready
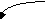

1
3
4
2
1. Process blocks for input
2. Scheduler picks another
process from
ready-to-run
3. Scheduler picks this
process
4. Input becomes available
Could be other events as well
output, mutex, timers, .... each
needs a state
External
event occurs